- Home
- Products
- Foot Protection
- Work Wear
- Hand Protection
- Head Protection
- Fall Protection
- Respiratory Protection
- Road Safety Equipment
- Emergency Safety
- New Product
- Greateagle
- News & Events
- Contact Us
In industries such as construction, oil and gas, utilities, telecommunications, and equipment maintenance, working at height is often unavoidable. However, falls from elevation continue to rank among the leading causes of workplace accidents and fatalities worldwide. According to OSHA statistics, falls account for a significant percentage of workplace injuries every year, which not only result in devastating human consequences but also lead to financial losses, downtime, and legal liabilities for employers.
To mitigate these risks, companies implement comprehensive fall protection systems, combining harnesses, anchor points, lifelines, and lanyards into a cohesive safety network. Within this system, the fall protection lanyard plays a central and irreplaceable role. Without a properly selected and maintained lanyard, even the most advanced body harnesses or anchorage devices cannot provide the required level of safety.
The lanyard acts as a critical safeguard by tethering the worker to a secure anchor point, thereby preventing uncontrolled free falls. In situations where workers are operating on scaffolds, ladders, rooftops, or elevated platforms, the presence of a lanyard can literally mean the difference between a safe recovery and a life-threatening accident. In this way, lanyards are not just accessories but essential lifesaving devices in any fall protection program.
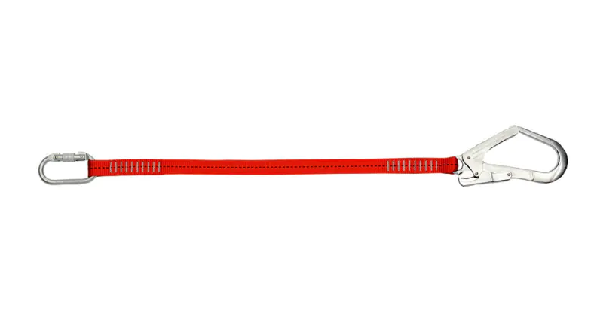
A fall protection lanyard is a specially engineered connecting device that links a worker’s safety harness to an approved anchorage point. It is typically manufactured from high-strength webbing, polyester, nylon, or rope materials, often reinforced with shock absorbers, energy-dissipating packs, or retractable mechanisms. These materials are chosen not only for their load-bearing capacity but also for their durability, resistance to abrasion, and ability to perform reliably in harsh industrial environments.
Definition: A fall protection lanyard is a flexible, load-rated connection component that ensures workers remain securely tied to a fall arrest system when operating at heights.
Purpose:
To prevent free falls by securing the worker to an anchor point.
To minimize fall distance so that, in case of a slip or loss of balance, the worker does not experience a dangerous drop.
To absorb and dissipate energy generated during a fall, thereby reducing the impact force transmitted to the worker’s body, the harness, and the anchorage structure.
Design Variety:
Lanyards come in multiple configurations, each designed to serve specific jobsite requirements. For instance:
Shock absorbing lanyards reduce arresting forces during falls.
Self-retracting lanyards (SRLs) allow greater mobility while maintaining constant tension and rapid fall arrest.
Twin-leg lanyards (Y-lanyards) enable continuous protection when workers need to move between anchor points.
Adjustable lanyards provide flexibility for tasks that require variable positioning.
This adaptability makes lanyards a versatile and indispensable element of modern fall protection systems.
The importance of using a properly selected fall arrest lanyard cannot be overstated, as it directly influences worker survival and injury prevention in the event of a fall. Below are the key reasons why lanyards are critical:
Fall Arrest:
Lanyards act as the primary fall arrest component within the safety system. By anchoring the worker securely, they stop a fall in progress before it reaches catastrophic momentum. This not only prevents ground impact but also reduces the likelihood of secondary injuries caused by collisions with surrounding structures.
Shock Absorption:
Advanced lanyards, particularly shock absorbing lanyards, are equipped with energy-dissipating devices that unfold or expand during a fall. This mechanism spreads the deceleration forces over a longer period of time, thereby reducing the impact force exerted on the worker’s body and spine. Without this shock absorption, even a short fall could generate enough force to cause severe injury or damage to safety equipment.
Mobility and Flexibility:
While safety is the primary goal, workers also need to move efficiently to perform their tasks. Adjustable lanyards, SRL lanyards, and twin-leg configurations allow workers to reposition themselves across different work zones without disconnecting from fall protection systems. This balance of mobility and security ensures that productivity is maintained without compromising safety.
Compliance with Safety Standards:
Regulatory agencies such as OSHA in the United States, ANSI Z359, and CSA in Canada strictly define requirements for fall protection equipment. Using compliant safety lanyards ensures that companies meet legal obligations, avoid penalties, and uphold workplace safety culture. More importantly, compliance demonstrates the employer’s commitment to worker well-being, reducing both liability and reputational risks.
By combining fall arrest, shock absorption, mobility, and compliance, lanyards stand as one of the most vital components in ensuring worker safety at height.
How They Work: Energy Absorption Explained
Shock-absorbing lanyards are among the most widely used forms of fall protection. They are designed with a built-in energy-absorbing component, typically a tear-away webbing pouch or a pack that deploys when subjected to high force. During a fall, instead of the worker experiencing an abrupt stop, the device gradually opens or extends, which lengthens the deceleration time. This process dramatically reduces the arresting force that would otherwise be transmitted directly to the worker’s body, the safety harness, and the anchorage point. Without this absorption mechanism, workers can sustain severe trauma, such as spinal compression or internal injuries, even if they survive the fall.
Benefits of Using Shock-Absorbing Lanyards
Helps ensure compliance with OSHA fall protection requirements, which limit maximum arresting force to 1,800 lbs.
Protects workers by lowering peak impact force, often cutting it down by more than 60% compared to non-shock options.
Reduces strain on anchor points and structural components, minimizing damage to equipment.
Provides peace of mind for employers and safety managers, as these lanyards are designed for high-risk situations.
When to Use Shock-Absorbing Lanyards
Shock-absorbing lanyards are especially valuable in industries such as construction, oil & gas, telecommunications, and maintenance. They should be used whenever workers are exposed to fall distances greater than a few feet, such as on scaffolding, towers, rooftops, or elevated platforms. They are also commonly used by window washers, tower climbers, and rigging professionals who face potential free fall scenarios daily.
Applications and Limitations
Non-shock absorbing lanyards are the simplest form of safety lanyard, typically made of durable rope, cable, or webbing. They create a fixed link between the harness and the anchor point but do not provide any reduction in fall impact. Because of this, their use in fall arrest applications is very limited. Instead, they are often used for work restraint, ensuring that workers cannot physically reach an edge or hazard where a fall could occur.
When Are Non-Shock Absorbing Lanyards Appropriate?
Useful in controlled environments such as warehouses, factory floors, or platforms with guardrails where fall hazards are minimal.
Effective for restraint systems, where the goal is prevention of reaching hazardous edges rather than arresting a fall.
Suitable in confined spaces or areas where fall clearance is so limited that a traditional fall arrest system would not function correctly.
Employers should note that non-shock absorbing lanyards must never be substituted for shock-absorbing lanyards in high-risk fall arrest situations, as this could lead to catastrophic injuries.
Benefits of Adjustable Length
Adjustable lanyards feature mechanisms—such as sliding adjusters or cam locks—that allow workers to shorten or lengthen the lanyard as needed. This customization helps reduce slack in the line, preventing unnecessary movement and lowering the chance of a fall. They also offer greater control over working positions, ensuring workers can maintain a safe, balanced stance without losing mobility.
Use Cases for Adjustable Lanyards
Utility pole work: Linemen can stay close to their anchor point while climbing or working at height.
Scaffold maintenance: Workers can adjust length to move across narrow work areas without creating tripping hazards.
Rope access and positioning tasks: Provides balance between stability and maneuverability.
Adjustable lanyards are particularly favored by professionals who must work in dynamic environments, where distance from the anchor point changes frequently.
How SRLs Provide Greater Mobility and Safety
Self-retracting lanyards (often called SRLs or retractable lifelines) are advanced devices that combine flexibility with safety. They use a spring-loaded mechanism that automatically extends and retracts the lifeline as the worker moves, keeping the line taut. This eliminates slack, which is a common source of dangerous free fall distance. If a fall occurs, the SRL instantly locks and activates an internal braking system that stops the fall within a few inches, significantly lowering impact forces and reducing overall fall distance.
Different Types of SRLs
Web SRLs: Lightweight and portable, making them suitable for indoor tasks and short-duration jobs.
Cable SRLs: Heavy-duty and resistant to abrasion, perfect for outdoor or rugged environments like construction or shipyards.
Leading Edge SRLs: Specially engineered for use around sharp edges or abrasive surfaces where standard SRLs may be damaged.
When to Use SRLs
SRLs are ideal for environments where workers need continuous mobility, such as on rooftops, assembly lines, or large-scale construction sites. They are also highly effective in jobs with multiple movement directions, where a fixed-length lanyard would hinder productivity or safety.
Continuous Fall Protection During Movement
Twin-legged, or Y-lanyards, have two separate connector legs that allow workers to move seamlessly between anchor points without ever disconnecting completely. This system guarantees 100% tie-off, meaning the worker is always secured by at least one lanyard leg, even when transitioning from one point to another.
Applications of Twin-Legged Lanyards
Tower climbing and telecommunications work, where multiple anchor points are common.
Bridge maintenance and steel erection, which require frequent repositioning across wide structures.
Oil rigs and industrial plants, where moving around complex frameworks demands continuous attachment.
Twin-leg lanyards are often the preferred choice for workers in dynamic, high-risk environments where mobility and uninterrupted protection are equally important.
The length of a fall protection lanyard directly impacts how far a worker can fall before the lanyard engages. Longer lanyards provide greater freedom of movement but can increase fall distance and potentially the arresting force. Conversely, shorter lanyards limit movement but reduce fall distance and help keep the impact force within safe limits. Choosing the correct length is crucial for both safety and productivity, particularly in environments with complex anchor points or confined spaces.
Lanyards are typically made from high-strength materials such as nylon or polyester, each offering unique benefits. Nylon is known for its elasticity, which provides some natural shock absorption, while polyester resists stretching under load, ensuring more predictable performance. The material selection affects not only the durability and longevity of the lanyard but also its resistance to environmental factors such as UV exposure, moisture, and chemicals.
The connectors—snap hooks, carabiners, or specialized locking hooks—are a critical part of a lanyard system. High-quality connectors are forged or heat-treated to withstand significant loads, often exceeding 5,000 lbs. Many come with swivel or locking mechanisms to prevent accidental disengagement and tangling. Proper selection of connectors ensures secure attachment to anchor points, maintaining worker safety and compliance with standards.
Each lanyard has a rated weight capacity, which typically includes the worker’s body weight plus any tools or equipment carried. Exceeding this limit compromises the effectiveness of the lanyard and increases the risk of injury. Understanding the maximum allowable weight, combined with the safety factor recommended by OSHA and ANSI Z359 standards, is essential when selecting the right lanyard for a specific job.
Fall protection lanyards must meet strict regulatory standards to ensure reliability. OSHA outlines minimum requirements for fall arrest systems, including maximum allowable arresting forces. ANSI Z359 series defines detailed performance criteria for lanyard design, testing, and use, while CSA standards provide guidance for Canadian workplaces. Using compliant lanyards helps protect workers and ensures organizations meet legal and insurance requirements.
The length of a fall protection lanyard directly impacts how far a worker can fall before the lanyard engages. Longer lanyards provide greater freedom of movement but can increase fall distance and potentially the arresting force. Conversely, shorter lanyards limit movement but reduce fall distance and help keep the impact force within safe limits. Choosing the correct length is crucial for both safety and productivity, particularly in environments with complex anchor points or confined spaces.
Lanyards are typically made from high-strength materials such as nylon or polyester, each offering unique benefits. Nylon is known for its elasticity, which provides some natural shock absorption, while polyester resists stretching under load, ensuring more predictable performance. The material selection affects not only the durability and longevity of the lanyard but also its resistance to environmental factors such as UV exposure, moisture, and chemicals.
The connectors—snap hooks, carabiners, or specialized locking hooks—are a critical part of a lanyard system. High-quality connectors are forged or heat-treated to withstand significant loads, often exceeding 5,000 lbs. Many come with swivel or locking mechanisms to prevent accidental disengagement and tangling. Proper selection of connectors ensures secure attachment to anchor points, maintaining worker safety and compliance with standards.
Each lanyard has a rated weight capacity, which typically includes the worker’s body weight plus any tools or equipment carried. Exceeding this limit compromises the effectiveness of the lanyard and increases the risk of injury. Understanding the maximum allowable weight, combined with the safety factor recommended by OSHA and ANSI Z359 standards, is essential when selecting the right lanyard for a specific job.
Fall protection lanyards must meet strict regulatory standards to ensure reliability. OSHA outlines minimum requirements for fall arrest systems, including maximum allowable arresting forces. ANSI Z359 series defines detailed performance criteria for lanyard design, testing, and use, while CSA standards provide guidance for Canadian workplaces. Using compliant lanyards helps protect workers and ensures organizations meet legal and insurance requirements.
| Inspection Check | Purpose | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Webbing / Rope Integrity | Detect cuts, frays, abrasion | Before each use | Check entire length; pay attention to edges |
| Stitching & Seams | Ensure load-bearing threads are intact | Before each use | Look for loose, broken, or worn threads |
| Connectors & Hooks | Verify locking mechanisms and deformation | Before each use & scheduled inspection | Ensure snap hooks and carabiners operate smoothly |
| Shock Absorber / SRL Mechanism | Confirm proper energy absorption function | Scheduled inspection | Test deployment if manufacturer allows |
| Corrosion & Chemical Damage | Prevent weakening of materials | Before each use | Check metal parts and webbing exposure to chemicals |
| Manufacturer Expiry / Service Life | Ensure lanyard is within safe usage period | Scheduled inspection | Retire equipment that exceeds recommended lifespan |
Selecting the proper fall protection lanyard begins with a thorough assessment of the work environment. Workers must identify potential fall hazards, such as unprotected edges, elevated platforms, scaffolds, or confined spaces. Environmental factors—like weather conditions, temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and presence of sharp edges—also influence lanyard choice. Proper assessment ensures the selected fall protection lanyard can withstand specific conditions and provide reliable protection.
Different tasks require different lanyard types. For example, maintenance on towers or high-rise structures benefits from twin-leg lanyards to maintain continuous attachment, while indoor facility work might only require a shock-absorbing lanyard for occasional movement. Self-retracting lanyards (SRLs) are ideal when maximum mobility is necessary. Choosing the right type enhances worker safety and productivity while preventing unnecessary restrictions on movement.
Understanding fall distance is critical when selecting a lanyard. Workers must consider the combined length of the lanyard, harness stretch, and anchor point height. This ensures that in the event of a fall, the worker will not contact the ground or obstacles. Calculations should also include a safety margin to account for dynamic forces and the deployment of shock absorbers. Accurate fall distance assessment prevents accidents and ensures compliance with OSHA fall protection regulations.
Fall protection systems are often composed of multiple components, including harnesses, anchor points, connectors, and lanyards. Compatibility between these elements is essential. Using connectors that fit improperly or lanyards incompatible with a harness can compromise the system’s effectiveness. Always verify manufacturer guidelines and ensure all components are certified to meet ANSI Z359 standards.
| Factor | Considerations | Recommended Lanyard Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work Environment | Height, obstacles, weather, chemical exposure | Shock-absorbing, SRL, twin-leg | Ensure material and design suit conditions |
| Task Type | Mobility needs, continuous attachment | Twin-leg, SRL, adjustable | Match lanyard to movement requirements |
| Fall Distance | Clearance from ground or hazards | Shock-absorbing, SRL | Include safety margins and harness stretch |
| Equipment Compatibility | Harness, anchors, connectors | All types | Verify compliance with ANSI Z359 and manufacturer guidelines |
| Weight & Load | Worker weight + tools | Shock-absorbing, SRL | Ensure rated capacity not exceeded |
The ProSafe Shock Absorbing Lanyard is designed for general construction and industrial applications. It features high-strength webbing with an integrated energy absorber that limits impact force during a fall. Lightweight and durable, this lanyard provides excellent mobility and comfort while meeting OSHA fall protection and ANSI Z359 standards.
SafeLine SRLs are ideal for high-mobility tasks such as tower maintenance and elevated inspections. The retractable lifeline automatically adjusts to the worker’s movement and instantly locks in the event of a fall. Its robust casing protects internal mechanisms, providing long-term reliability and superior safety performance.
TwinGuard lanyards offer continuous fall protection during transitions between anchor points. Each leg is equipped with a shock absorber, ensuring that workers remain securely tethered at all times. Perfect for scaffolding, ladder work, and maintenance, TwinGuard enhances safety while minimizing downtime.
FlexiLanyard adjustable lanyards allow workers to modify the length of their lanyard on-site to accommodate varying anchor heights or work environments. Made from premium webbing and reinforced connectors, they combine versatility with compliance to ANSI Z359 and OSHA standards.
UltraSafe rope lanyards are constructed from durable polyester rope with high elasticity for energy absorption. They are suitable for confined space entry and rescue operations. The lightweight design ensures comfort, while robust connectors maintain secure attachment to anchor points.
MaxLock features a shock-absorbing core and a swivel snap hook that prevents twisting during movement. Its ergonomic design and high load capacity make it suitable for general industry, utilities, and construction, meeting all regulatory compliance standards.
QuickConnect SRLs offer rapid deployment and ease of use, with a retractable lifeline that locks automatically upon sudden descent. Ideal for maintenance and inspection personnel working at varying heights, it provides both flexibility and reliable fall arrest capability.
ProTwin’s dual-leg design ensures workers are always connected to an anchor point, minimizing risk during movement between workstations. Integrated energy absorbers limit fall impact, making it suitable for tower, scaffolding, and elevated platform work.
LiteGuard is a compact, lightweight lanyard designed for reduced fatigue during extended use. Its shock-absorbing system ensures safety while remaining comfortable for long shifts. It is widely used in indoor maintenance and light construction applications.
RescuePro combines an adjustable-length design with self-retracting functionality, providing optimal mobility and fall protection. Suitable for rescue operations, high-rise maintenance, and complex work environments, it ensures worker safety without compromising movement.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets minimum requirements for fall protection equipment to ensure worker safety across industries. OSHA regulations cover the design, performance, and proper use of fall protection lanyards and associated equipment. Compliance with OSHA standards helps prevent workplace injuries, reduces liability, and ensures that employers maintain a safe working environment. Key OSHA guidelines specify maximum allowable free-fall distances, proper anchor point strength, and regular inspection and maintenance of lanyards.
The ANSI Z359 series is the primary standard for fall protection equipment in the United States. It provides detailed specifications for lanyard types, energy absorption, strength requirements, and connector performance. Lanyards certified under ANSI Z359 undergo rigorous testing to verify their durability and effectiveness under real-world conditions. Compliance ensures that the fall arrest lanyard performs reliably during a fall, safeguarding workers and meeting industry best practices.
In Canada, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) sets requirements for fall protection systems. CSA standards address lanyard construction, inspection frequency, and compatibility with harnesses and anchorage systems. Following CSA guidelines ensures that workplaces meet legal requirements for occupational safety and that workers are protected in accordance with national regulations.
Other regions have their own regulations governing fall protection equipment, including lanyards. For example, European standards (EN 354 and EN 355) specify requirements for lanyard design, strength, and shock absorption. International compliance ensures that equipment can be safely used in multiple regions, providing uniform protection for workers across global operations.
| Standard | Region | Key Focus | Lanyard Requirements | Testing/Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSHA 1926 | USA | Construction, general industry | Maximum fall distance, anchor strength, inspection | Mandatory workplace inspections, adherence to OSHA limits |
| ANSI Z359 | USA | Comprehensive fall protection | Energy absorption, connector strength, lanyard performance | Lab-tested for tensile strength, shock load, and durability |
| CSA Z259 | Canada | Worker safety in heights | Lanyard length, shock absorption, compatibility | Routine inspections, certified by CSA |
| EN 354 / EN 355 | Europe | Personal fall protection | Webbing, rope, energy absorber standards | Third-party testing, CE marking required |
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting a lanyard that does not match the specific task or work environment. For example, using a non-shock absorbing lanyard in a high-risk construction zone could result in excessive fall impact, while an SRL may be overkill for short-duration indoor maintenance. Understanding the differences between shock absorbing lanyards, SRL lanyards, twin-leg lanyards, and adjustable lanyards is crucial to ensure both safety and efficiency.
Incorrectly attaching a lanyard to the harness or anchor point is a common cause of accidents. Connectors such as snap hooks and carabiners must be fully locked, oriented properly, and secured to approved anchor points. Failure to properly connect a fall protection lanyard can render even the strongest lanyard ineffective during a fall.
Skipping regular inspection of lanyards is a serious safety oversight. Pre-use checks, scheduled inspections, and monitoring for wear, corrosion, or damaged hardware are mandatory to maintain reliability. Ignoring inspection guidelines can allow compromised equipment to remain in use, increasing the risk of injury.
Every lanyard has a maximum rated weight, including the worker and any carried tools or equipment. Exceeding this limit can lead to failure of the fall arrest lanyard during a fall. It is critical to verify the weight rating before use and account for any additional load.
Even minor damage, such as frayed webbing, faded material, or compromised connectors, can significantly reduce a lanyard’s strength. Lanyards must be immediately retired if any damage is detected. Using worn-out fall protection lanyards not only violates safety standards but can also result in serious accidents.
Proper maintenance begins with regular inspection. Lanyards should be checked for webbing integrity, stitching, connectors, and shock-absorbing components before every use and during scheduled inspections. Identifying signs of wear, fraying, chemical damage, or UV degradation early helps prevent failures. Routine inspections are crucial to ensure the fall protection lanyard continues to perform reliably and protects workers effectively.
Dirt, oil, chemicals, and moisture can compromise lanyard performance over time. Cleaning should be performed according to manufacturer recommendations, typically using mild soap and water. Lanyards should never be exposed to harsh solvents, bleach, or abrasive cleaning methods, as these can weaken the material. After cleaning, lanyards must be fully dried in a shaded, ventilated area to prevent mildew or degradation.
Even with proper inspection and cleaning, lanyards have a finite lifespan. Components such as shock absorbers, connectors, and swivels may need replacement separately, depending on wear. If any part shows damage, the lanyard should either be repaired by a qualified professional or retired from service. Ensuring all components are in optimal condition is vital for worker safety.
Storage plays a critical role in prolonging lanyard life. Lanyards should be stored in a clean, dry environment, away from direct sunlight, extreme heat, and chemical exposure. Hanging lanyards or keeping them in protective bags prevents unnecessary kinks or abrasion, maintaining both the integrity and flexibility of the equipment.
Fall protection lanyards are designed to secure workers at heights by connecting their harness to a reliable anchor point. They prevent free falls, reduce fall distance, and minimize the impact forces on the body. These lanyards are essential in construction, maintenance, utilities, and any industry where workers operate above ground level.
Shock absorbing lanyards contain a built-in energy absorber that elongates during a fall, reducing the peak force on the worker. This controlled energy dissipation lowers the risk of injury, making them suitable for situations where falls are possible but anchor points are fixed.
SRL lanyards are ideal when workers require maximum mobility while remaining protected. The retractable lifeline automatically adjusts to the worker’s movement and locks instantly if a fall occurs. Use SRLs for tasks like tower work, elevated inspections, or any activity requiring frequent movement along anchor points.
Twin-leg lanyards (Y-lanyards) allow workers to stay continuously connected while moving between anchor points, reducing the risk of free-fall incidents during transitions. Single-leg lanyards provide protection when moving is minimal or when only one secure anchor point is needed. Selecting the correct lanyard type is crucial for both safety and operational efficiency.
Pre-use inspections are mandatory before each shift, while scheduled inspections by a competent person should occur monthly or quarterly depending on usage intensity. Inspection includes checking webbing, connectors, stitching, and shock absorbers for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Regular inspections ensure the lanyard remains reliable and compliant with OSHA and ANSI standards.
Yes, but only if the lanyard is specifically rated for exposure to chemicals, UV light, extreme temperatures, or moisture. Material choice, such as nylon or polyester, and the design of connectors play a crucial role in durability. Always verify manufacturer specifications for environmental resistance before use.
A lanyard must be retired if it shows any sign of damage, wear, or failed components. Manufacturers also specify a maximum service life, typically based on material type and usage conditions. Retiring lanyards on time prevents equipment failure and ensures ongoing worker safety.
Reliable lanyards meet regulatory standards such as OSHA fall protection, ANSI Z359, CSA, or relevant international standards. Compliance ensures that the lanyard has been tested for strength, energy absorption, and overall performance, providing confidence that it will perform as intended in the event of a fall